GEO Ranking Factors have fundamentally changed how brands achieve digital visibility in 2023.
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) helps content rank better in AI-generated answers across large language models (LLMs).
Your brand's success in this new digital world depends on how frequently it appears in generative answers.
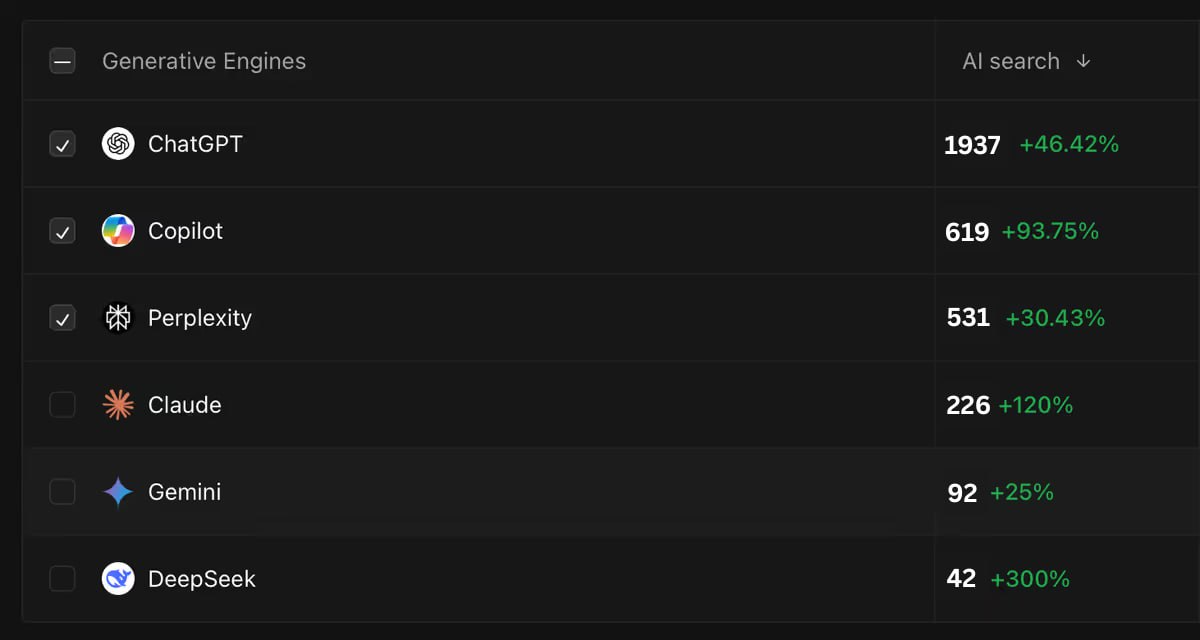
- ChatGPT dominates the U.S. market with a 61.3% share, while Google Gemini holds 13.3%.
This makes understanding geo ranking crucial for digital visibility today. Language models work differently than Google's bot, they value high-quality, trusted, and well-laid-out content.
We at Lureon understand that AI visibility needs a unique content optimization strategy. Our geo ranking priorities align with what LLMs value most: clarity, authority, structure, and relevance.
This piece will guide you through the key ranking factors for AI visibility.
You'll learn how we at Lureon optimize content to make it a go-to source for generative AI responses.
Key Takeaways
- AI visibility is binary - Content either appears in AI responses or remains completely invisible, making optimization critical for maintaining digital presence.
- Entity optimization drives recognition - Proper Named Entity Recognition (NER) and consistent brand mentions across platforms increase AI citation rates by 400%.
- Semantic structure beats keywords - Topic clusters and descriptive internal linking help LLMs understand content relationships better than traditional keyword density.
- Schema markup provides 4.3x advantage - Structured data with FAQPage, Article, and Organization schemas dramatically improves AI citation rates over unstructured content.
- AI traffic converts 4.4x better - While AI reduces overall clicks by 34.5%, the traffic that does convert from AI-generated answers shows significantly higher engagement rates.
How Lureon Aligns Content with LLM Ranking Behavior
Lureon sees a clear transformation in how content ranks in different systems. Content optimization methods that worked for traditional search engines don't cut it anymore in the AI-powered digital world.
Your content either shows up in responses or stays hidden.
Understanding AI Summarization vs. Traditional Ranking
Search engines and AI platforms process information in completely different ways. Search engines rank web pages based on keywords and backlinks.
LLMs blend information from big datasets that include web content, books, research papers, and forums. This creates new ways to optimize content.
LLMs go beyond counting keywords.
They analyze content quality through complex interpretation and look for:
- Content relevance and authority from trusted sources
- Structured, consistent information with clear metadata
- Verifiable claims supported by credible sources
- Unique information gain rather than recycled content
These differences matter a lot.
AI Overviews cut clicks by 34.5% compared to similar informational keywords without an AI Overview. Google searches now lead to no clicks 60% of the time because answers appear right on results pages.
In spite of that, new doors have opened.
Traffic from AI-powered results converts 4.4× better than traditional search traffic. This shows users who click through AI-generated content are more likely to take action.
Optimizing for Extractive vs. Abstractive Models
Content optimization varies based on whether we target extractive or abstractive AI models.
These two approaches show how AI systems create summaries and answers differently.
1. Extractive summarization picks and uses direct passages from source content.
LLMs do this well, so content needs specific formatting for extraction.
We create "prompt surfaces", semantic structures that LLMs naturally pick when citing passages. This means using question-style headers that match user queries and keeping answers under 300 characters where possible.
2. Abstractive summarization creates new content by understanding the source material.
This method can introduce errors through hallucinations, content not found in the original source.
- We use Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) techniques to help models line up with specific priorities.
Our Preference Ranking Optimization (PRO) takes pair-wise contrast further to handle preference rankings of various lengths. This method turns human alignment into matching the probability ranking of LLM-generated responses with human preference ranking.
The numbers tell the story.
Companies that follow our structured approach have seen their AI citation rate jump by 400% just by adding proper citations.
Our tests show that content with schema markup gets cited 4.3x more often in AI search results than unstructured content.
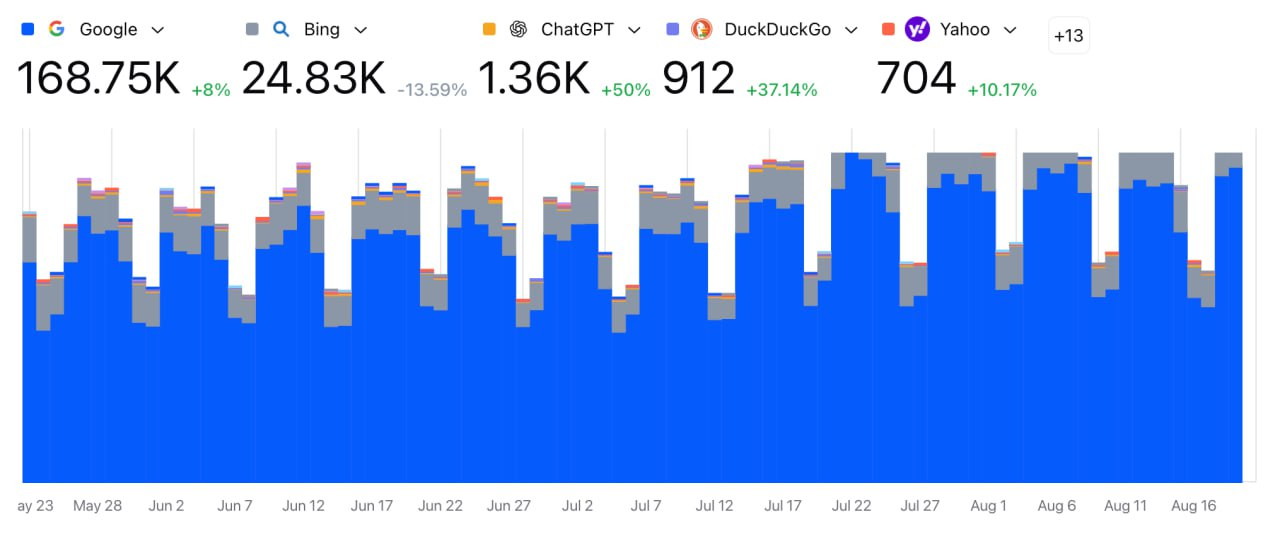
ChatGPT's weekly active users have grown 8× to over 800 million.
Becoming skilled at these GEO ranking factors is crucial to stay visible in this fast-changing digital world.
Entity Optimization and Brand Recognition in GEO
Entity optimization is the life-blood of successful GEO ranking factors.
AI systems now rely more on recognizing and contextualizing named entities in content.
Our team at Lureon has found that AI-driven search looks beyond keywords. It seeks complete, coherent entities that signal what content truly represents.
Entity Salience in ChatGPT and Gemini
Entity salience shows how relevant and important specific entities are within content.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning review the prominence of these entities.
Both ChatGPT and Gemini show clear priorities for entities that appear regularly in high-quality sources from their training data.
To name just one example, see how automotive domains show stabilized, curated lists of prominent examples within ChatGPT. Published rankings, award results, review frequencies, and brand visibility in user queries shape these lists.
These entities serve as default "anchors," especially in comparative or ranking prompts.
The salience score calculation depends on these vital factors:
- Entity recognition and assigned weightage
- Significance and frequency of appearance
- Position of entities (earlier mentions carry more weight)
- Contextual relevance within the document
- Interconnectedness between various entities
Our team at Lureon makes entity optimization a top priority.
AI engines value clarity over keyword density, citations over fluff, and structure over style. AI cares about credibility, consistency, and context, not follower counts or branded search volume.
Using Named Entity Recognition (NER) for Clarity
Named Entity Recognition (NER) extracts and classifies information like names, organizations, and locations within text into predefined categories. NER becomes crucial as AI doesn't just scan content, it breaks down and interprets meaning.
Ahrefs research shows brand mentions, branded anchors, and brand search volume are the most important visibility factors for LLMs and AI search tools.
We improve NER implementation through several key approaches:
- Our first step involves auditing terminology and listing every product name, feature, use case, and industry term. This consistent usage of phrasing and abbreviations helps AI models classify entities accurately.
- Next, we add schema markup carefully. Organization schema helps LLMs link brand names to actual businesses, while Local Business schema works for businesses with physical locations.
Our tests prove that content with schema markup gets 4.3x more citations in AI search results than unstructured content.
- We then analyze context by exploring relationships between words through vector representations. This keeps recognized entities relevant to context.
Unstructured data makes up 80-90% of all data, making NER essential to convert this information into meaningful patterns.
- Before publishing, we check entity consistency across all channels, website, social profiles, and repositories like GitHub and Wikidata.
These sources give AI systems the information needed to recognize specific brands.
We also improve on-page elements through proper meta descriptions and strategic links to boost entity salience.
This methodical approach to entity optimization has helped our clients improve their GEO performance.
The focus has changed from clicks to credibility, from page optimization to model training.
Semantic Structuring and Internal Linking for GEO
Semantic structuring serves as the foundation of effective GEO ranking strategies.
Our work at Lureon has shown that LLMs process content relationships differently from traditional search engines. This makes proper content organization vital for AI visibility.
Topic Clusters and Semantic Relationships
AI systems process and recommend information based on semantic relationships between content pieces.
LLMs group related words and phrases naturally, and content that's properly organized creates meaningful associations that boost visibility.
A pillar page focusing on core themes stands at the center of topic clusters, while cluster pages covering sub-themes connect through hierarchical URLs and internal links.
These clusters fulfill several vital functions for AI visibility:
- Signal topical authority - Your expertise shines through to search engines and AI systems when you provide complete coverage
- Create semantic neighborhoods - Content organization helps AI grasp conceptual relationships
- Improve content discovery - Well-laid-out clusters let LLMs find your content quickly
Our experience at Lureon proves that topic clusters match perfectly with LLM's information processing. AI search uses semantic similarity to calculate meaning-based connections between texts, unlike traditional keyword matching.
This method retrieves information better, especially with varied language use, ambiguity, and evolving terminology.
Science backs this approach strongly. Clear semantic relationships emerge when content follows proper structure.
- We map out content relationships to keep the structure clear and spot coverage gaps.
Each cluster piece then links to the pillar content and other relevant cluster pieces.
Anchor Text Optimization for AI Interpretability
Anchor text, the visible, clickable text within a hyperlink, helps AI systems understand content relationships.
Descriptive anchor text does more than traditional SEO.
It provides context about linked pages and shapes how LLMs interpret and index your content.
Our anchor text principles focus on several key aspects:
- Relevance comes first. Your anchor text should mirror the linked page's content accurately. This matters both for user experience and for sending clear signals to AI systems about content relationships.
- Natural link profiles need varied anchor text types. We mix exact-match, partial-match, branded, and descriptive anchor texts to show organic linking patterns rather than manipulation.
- Topic relevance grows stronger with consistency. Users and AI systems might get confused if you use different anchor text for the same link across your website.
- Semantic descriptiveness matters more than keyword density. Strategic relationships that expand content's reach and relevance emerge from AI-powered internal linking.
Semantic structuring and internal linking create essential communication channels between your content and AI systems.
LLMs understand your content's structure, relationships, and expertise better when you organize content into logical clusters with descriptive internal links.
These elements prove essential for securing prominent placement in AI-generated answers.
Formatting and Schema for AI-Friendly Content
Web page structure plays a crucial role in how LLMs interpret content, not just its quality.
Our team at Lureon discovered that good formatting and schema setup are basic GEO ranking factors that boost AI visibility.
1. Semantic HTML Tags:
Semantic HTML gives LLMs clear signals about content purpose and structure. These elements tell machines what the content means, unlike basic tags.
Here are the most useful tags we use:
- The
<article>tag - Shows independent, complete content pieces like blog posts, news articles, and product descriptions. This helps LLMs spot content boundaries and cite sources better. - The
<section>tag - Groups related content with headings. This lets LLMs understand how different parts connect. - The
<table>tag - Presents data in a grid that AI systems can read more easily.
LLMs that don't crawl as well as Google need this clean, structured HTML.
Think of semantic markup as a bridge between your content and machine understanding.
2. Schema Types Used: FAQPage, Article, Organization
Schema markup helps LLMs understand content quickly and accurately.
We focus on three schema types that make the biggest difference:
- FAQPage Schema: Shows question-answer pairs clearly, which helps match user questions with expert answers
- Article Schema: Tells AI systems when content was published, who wrote it, and what type it is
- Organization Schema: Lets LLMs know your brand is a real company and links it to trusted sources
Good schema creates a layer that defines relationships in machine-readable format.
Our research shows content with schema gets cited 4.3x more often in AI search results.
3. Meta Title and Description Optimization for LLMs
Meta data shows LLMs what your content covers.
- Better metadata means your content appears more often in AI-generated answers.
Meta titles should be short (50-60 characters) and use keywords that match what users want.
Meta descriptions need to sum up content in 155-160 characters. They should focus on user needs and naturally include secondary keywords.
Titles, meta descriptions, and H1s should work together to show what each page is about. This consistency helps AI systems understand your content's focus and value.
Performance Monitoring and GEO Auditing at Lureon
Knowing how to measure our GEO implementations success helps us maintain AI visibility.
Our team at Lureon has built reliable monitoring systems to measure and enhance LLM performance.
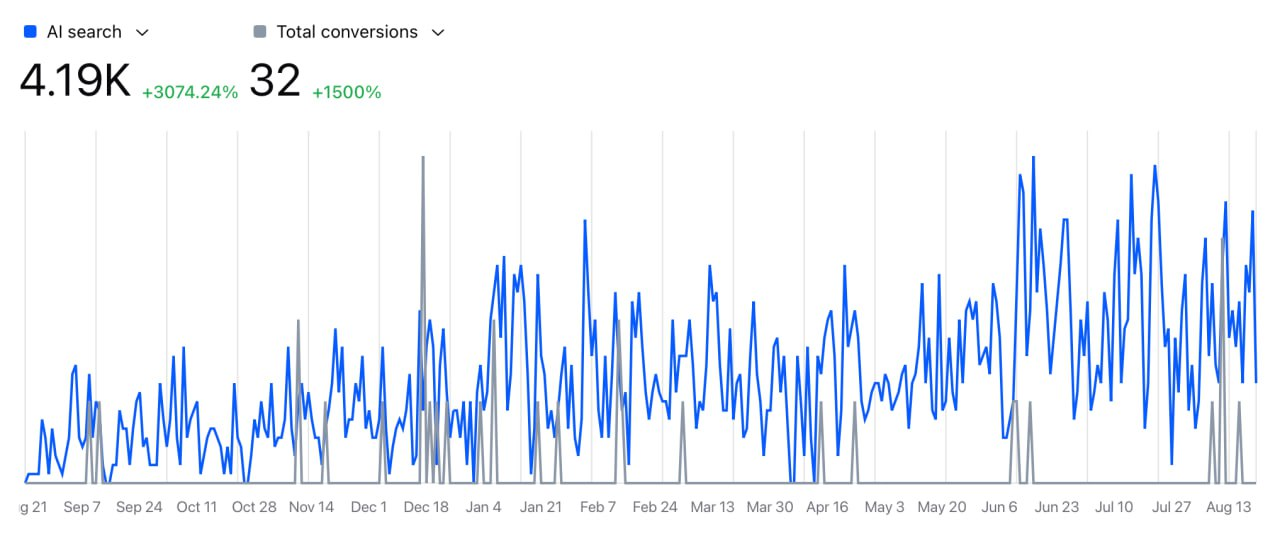
Real-Time LLM Citation Tracking Tools
We use specialized tools that track live AI responses through front-end monitoring and synthetic queries across ChatGPT, Claude, Google AI, and Perplexity.
These platforms measure vital metrics including share of voice, which shows the percentage of AI answers that mention your brand compared to total answers for target queries.
Brands that perform well typically capture ≥15% share across core query sets while enterprise leaders reach 25-30% in specialized verticals.
GEO Scorecard for Content Evaluation
Our GEO Scorecard looks at content through three aspects:
- Authority: This checks if content links to credible sources and supports claims with citations.
- Readability: Shows how available the content is to readers of all levels.
- Structure: Checks if passages have clear headings and snippet-ready formatting.
This analysis creates a clear path to optimize content for AI engines.
Prompt Testing and Semantic Gap Analysis
Our systematic prompt optimization testing has shown notable improvements in different use cases.
Optimized prompts have shown an 18% boost in summarization tasks, 8% in dialog completion, and 22% in function calling standards.
Beyond technical optimization, we run semantic gap analysis to find where content doesn't answer user questions from an AI's point of view.
This helps us connect known user intents from search queries to the new world of LLM prompts.
Conclusion
Success needs a strategic approach that focuses on clarity, authority, structure, and relevance, these are what LLMs look for when they generate responses.
Our team at Lureon has found that good AI visibility needs entity optimization with proper NER setup, detailed semantic structuring with meaningful topic clusters, and careful HTML formatting with schema markup.
These elements decide if AI will use your content or ignore it completely.
AI-driven search brings new challenges and opportunities.
Companies that adapt quickly gain a competitive edge.
Get started with Lureon today and watch your company chow up on the top of AI search.
FAQs:
1. What are the key differences between traditional SEO and GEO (Generative Engine Optimization)?
GEO focuses on optimizing content for AI-generated answers, prioritizing clarity, authority, structure, and relevance. Unlike traditional SEO, GEO success is measured by how often a brand appears in generative answers, with visibility being binary, content either appears in AI responses or remains invisible.
2. How does entity optimization impact AI visibility?
Entity optimization significantly improves AI visibility by helping language models recognize and contextualize named entities in content. Proper implementation of Named Entity Recognition (NER) and consistent brand mentions across platforms can increase AI citation rates by up to 400%.
3. What role does semantic structuring play in GEO?
Semantic structuring is crucial for GEO as it helps AI systems understand content relationships. Organizing content into topic clusters with descriptive internal linking enables language models to interpret your content's structure, relationships, and expertise more effectively, improving the chances of appearing in AI-generated answers.
4. How important is schema markup for AI visibility?
Schema markup is extremely important for AI visibility. Content with proper schema implementation, particularly FAQPage, Article, and Organization schemas, receives 4.3 times more citations in AI search results compared to unstructured content. It provides critical context that helps AI systems interpret content efficiently.
5. What metrics are used to measure GEO performance?
Key metrics for measuring GEO performance include share of voice (percentage of AI answers mentioning your brand), GEO scorecard evaluations (assessing content authority, readability, and structure), and semantic gap analysis. Real-time LLM citation tracking tools are also used to monitor performance across various AI platforms.
